from tsfast.datasets import create_dls_testLearner
dls = create_dls_test()model = SimpleRNN(1,1)
lrn = Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss()).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.055792 | 0.059331 | 00:01 |
Callbacks
GradientClipping
GradientClipping (clip_val=10)
Callback cutts of the gradient of every minibtch at clip_val
model = SimpleRNN(1,1)
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=GradientClipping(10)).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.057712 | 0.060895 | 00:01 |
GradientNormPrint
GradientNormPrint (after_create=None, before_fit=None, before_epoch=None, before_train=None, before_batch=None, after_pred=None, after_loss=None, before_backward=None, after_cancel_backward=None, after_backward=None, before_step=None, after_cancel_step=None, after_step=None, after_cancel_batch=None, after_batch=None, after_cancel_train=None, after_train=None, before_validate=None, after_cancel_validate=None, after_validate=None, after_cancel_epoch=None, after_epoch=None, after_cancel_fit=None, after_fit=None)
Callback prints the norm of the gradient of every minibtch
model = SimpleRNN(1,1)
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=GradientNormPrint()).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.058281 | 0.060542 | 00:01 |
Gradient norm: 0.32
Gradient norm: 0.27
Gradient norm: 0.25
Gradient norm: 0.15
Gradient norm: 0.07
Gradient norm: 0.02
Gradient norm: 0.04
Gradient norm: 0.04
Gradient norm: 0.13
Gradient norm: 0.09
Gradient norm: 0.06
Gradient norm: 0.06GradientBatchFiltering
GradientBatchFiltering (filter_val=10)
Callback skips batches with a gradient norm larger than filter_val
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=GradientBatchFiltering(11.0)).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.052950 | 0.052226 | 00:01 |
WeightClipping
WeightClipping (module, clip_limit=1)
Callback that clips the weights of a given module at clip_limit after every iteration
model = SimpleRNN(1,1)
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=WeightClipping(model,clip_limit=1)).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.054952 | 0.058467 | 00:01 |
SkipFirstNCallback
SkipFirstNCallback (n_skip=0)
Callback skips first n samples from prediction and target, optionally with_loss
SkipNaNCallback
SkipNaNCallback (after_create=None, before_fit=None, before_epoch=None, before_train=None, before_batch=None, after_pred=None, after_loss=None, before_backward=None, after_cancel_backward=None, after_backward=None, before_step=None, after_cancel_step=None, after_step=None, after_cancel_batch=None, after_batch=None, after_cancel_train=None, after_train=None, before_validate=None, after_cancel_validate=None, after_validate=None, after_cancel_epoch=None, after_epoch=None, after_cancel_fit=None, after_fit=None)
Callback skips minibatches with a NaN loss
CancelNaNCallback
CancelNaNCallback (after_create=None, before_fit=None, before_epoch=None, before_train=None, before_batch=None, after_pred=None, after_loss=None, before_backward=None, after_cancel_backward=None, after_backward=None, before_step=None, after_cancel_step=None, after_step=None, after_cancel_batch=None, after_batch=None, after_cancel_train=None, after_train=None, before_validate=None, after_cancel_validate=None, after_validate=None, after_cancel_epoch=None, after_epoch=None, after_cancel_fit=None, after_fit=None)
Callback cancels trainig minibatches with a NaN loss
VarySeqLen
VarySeqLen (min_len=50)
Callback varies sequence length of every mini batch
model = SimpleRNN(1,1)
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=VarySeqLen(10)).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.061609 | 0.061791 | 00:01 |
sched_lin_p
sched_lin_p (start, end, pos, p=0.75)
sched_ramp
sched_ramp (start, end, pos, p_left=0.2, p_right=0.6)
init_sz = 200
pred_sz = 600
win_sz = init_sz+pred_sz
truncate_length = init_sz+10
plt.figure()
plt.plot([win_sz-sched_lin_p(win_sz-truncate_length,0,pct) for pct in np.linspace(0,1,100)])
plt.plot([win_sz-sched_ramp(win_sz-truncate_length,0,pct,0.2,0.6) for pct in np.linspace(0,1,100)])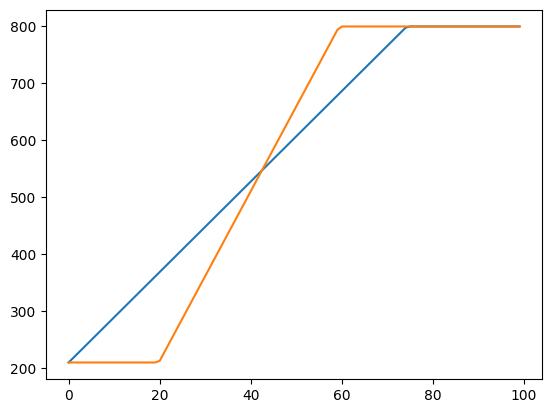
CB_TruncateSequence
CB_TruncateSequence (truncate_length=50, scheduler=<function sched_ramp>)
Callback varies sequence length of every mini batch
model = SimpleRNN(1,1)
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=CB_TruncateSequence(50,sched_lin_p)).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.055499 | 0.057812 | 00:01 |
CB_AddLoss
CB_AddLoss (_loss_func, alpha=1.0)
Callback that adds the results of a given loss_function to the mini_batch after the original loss function has been applied
model = SimpleRNN(1,1)
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=CB_AddLoss(nn.MSELoss(),alpha=10)).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.629243 | 0.059755 | 00:01 |
# #| export
# class BatchLossFilter(Callback):
# """
# Callback that selects the hardest samples in every batch representing a percentage of the total loss.
# """
# def __init__(self, loss_perc=1., filter_criterion=nn.HuberLoss(reduction='none'), schedule_func:Optional[callable]=None):
# store_attr() # Stores all passed arguments as class attributes
# def before_batch(self):
# """
# Selects hardest samples before processing each batch.
# """
# if not self.training: return # Skip if not in training mode
# if self.schedule_func is None: loss_perc = self.loss_perc
# else: loss_perc = self.loss_perc * self.schedule_func(self.pct_train) # Adjust loss_perc if a schedule function is given
# if loss_perc == 1.: return # If loss_perc is 1, all samples are included, no need to filter
# with torch.no_grad(): # No gradients needed for the filtering operation
# losses = self.filter_criterion(self.learn.model(self.x), self.y) # Compute individual losses
# if losses.ndim >= 2: losses = losses.mean(tuple(range(1,losses.ndim))) # If loss is multi-dimensional, take the mean over all but the first dimension
# losses /= losses.sum() # Normalize losses to make them sum up to 1
# idxs = torch.argsort(losses, descending=True) # Sort indices by loss
# cut_idx = max(1, torch.argmax((losses[idxs].cumsum(0) > loss_perc).float())) # Determine the cut-off index where cumulative sum exceeds loss_perc
# idxs = idxs[:cut_idx] # Select the hardest samples
# self.learn.xb = tuple(xbi[idxs] for xbi in self.learn.xb) # Filter the input batch
# self.learn.yb = tuple(ybi[idxs] for ybi in self.learn.yb) # Filter the output batchBatchLossFilter
BatchLossFilter (loss_perc=1.0, filter_criterion=HuberLoss(), schedule_func:Optional[<built-infunctioncallable>]=None)
Callback that selects the hardest samples in every batch representing a percentage of the total loss.
# #| export
# class BatchLossFilter(Callback):
# """
# Callback that selects the hardest samples in every batch representing a percentage of the total loss.
# """
# order = -9
# def __init__(self, loss_perc=1., filter_criterion=nn.HuberLoss(reduction='none'), schedule_func:Optional[callable]=None):
# store_attr()
# def after_pred(self):
# """
# Calculate losses and select hardest samples after model prediction and before loss computation.
# """
# if not self.training: return # Skip if not in training mode
# if self.schedule_func is None: loss_perc = self.loss_perc
# else: loss_perc = self.loss_perc * self.schedule_func(self.pct_train) # Adjust loss_perc if a schedule function is given
# if loss_perc == 1.: return # If loss_perc is 1, all samples are included, no need to filter
# with torch.no_grad(): # No gradients needed for the filtering operation
# losses = self.filter_criterion(self.pred, *self.learn.yb) # Compute individual losses with model's predictions
# if losses.ndim >= 2: losses = losses.mean(tuple(range(1,losses.ndim))) # If loss is multi-dimensional, take the mean over all but the first dimension
# losses /= losses.sum() # Normalize losses to make them sum up to 1
# idxs = torch.argsort(losses, descending=True) # Sort indices by loss
# cut_idx = max(1, torch.argmax((losses[idxs].cumsum(0) > loss_perc).float())) # Determine the cut-off index where cumulative sum exceeds loss_perc
# self.idxs = idxs[:cut_idx] # Store the indices of the hardest samples
# def after_loss(self):
# """
# Recalculate the loss with the selected hardest samples.
# """
# if not self.training: return # Skip if not in training mode
# self.learn.loss_grad = self.loss_func(self.pred[self.idxs], *(yb[self.idxs] for yb in self.learn.yb)) # Compute the loss with hardest samplesmodel = SimpleRNN(1,1)
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=BatchLossFilter(loss_perc=0.8)).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.074184 | 0.059581 | 00:03 |
TimeSeriesRegularizer
TimeSeriesRegularizer (alpha=0.0, beta=0.0, dim=None, detach=False, modules=None, every=None, remove_end=True, is_forward=True, cpu=True, include_paramless=False, hook=None)
Callback that adds AR and TAR to the loss, calculated by output of provided layer
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=[TimeSeriesRegularizer(1.0,1.2,modules=[model.rnn])]).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.053709 | 0.054955 | 00:01 |
ARInitCB
ARInitCB (after_create=None, before_fit=None, before_epoch=None, before_train=None, before_batch=None, after_pred=None, after_loss=None, before_backward=None, after_cancel_backward=None, after_backward=None, before_step=None, after_cancel_step=None, after_step=None, after_cancel_batch=None, after_batch=None, after_cancel_train=None, after_train=None, before_validate=None, after_cancel_validate=None, after_validate=None, after_cancel_epoch=None, after_epoch=None, after_cancel_fit=None, after_fit=None)
Adds the target variable to the input tuple for autoregression
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss()).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.037985 | 0.027872 | 00:01 |
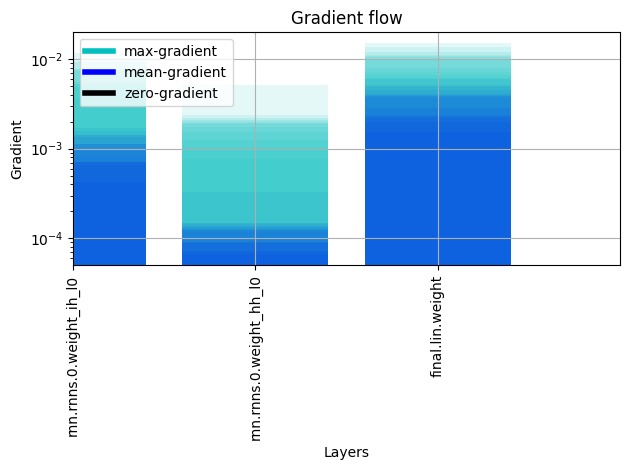
plot_grad_flow
plot_grad_flow (named_parameters)
Plots the gradients flowing through different layers in the net during training. Can be used for checking for possible gradient vanishing / exploding problems. modified version of https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/check-gradient-flow-in-network/15063/8*
Call multiple time for transparent overlays, representing the mean gradients*
CB_PlotGradient
CB_PlotGradient (n_draws=20)
Plot the Gradient Distribution for every trainable parameter
Learner(dls,model,loss_func=nn.MSELoss(),cbs=CB_PlotGradient()).fit(1)| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.021996 | 0.018407 | 00:01 |